CAUSES
ENDOCRINE DISORDERS
- Diabetes
- Adrenal Gland Disease
- Hypogonadism
- Hyperprolactemia
Diabetes can cause Erectile Dysfunction because it can damage the blood supply to penis and the nerves that are responsible for erection. During the arousal, nitric oxide is released in the blood stream that results in the relaxation of the muscles and the arteries, which allows more blood to flow into the penis and results in Erection. In case of Diabetes, the blood sugar level swings, and less nitric oxide is produced when blood sugar levels are high. This results in limited flow of blood into the penis and results in Erectile Dysfunction.
The proper erection mechanism depends on correct interrelationship between neurological, vascular, psychological and hormonal factors. Endocrine diseases affect sexual activity and leads to sexual dysfunction. Diabetes mellitus is the most frequently occurring endocrine disease causing erectile dysfunction due to the frequent vascular and neurological complications associated. Hyperprolactinemia causes disorders of the sexual sphere because it produces a descent of testosterone. Thyroid hormone disorders both (hyper and hypothyroidism) are associated with erectile dysfunction, which will subside in half the patients with thyroid hormone normalization. The role of adrenal hormones in erectile function is not clear. Among endocrine- metabolic disorders, hypercholesterolemia as an important risk factor for erectile dysfunction.
NEUROGENIC DISORDERS
- Spinal cord injury
- Parkinson’d disease
- Psychogenic
- Epilepsy
Neurogenic cause of Erectile Dysfunction may have its origin in the central or peripheral nervous system. Possible process of erectile dysfunction of central origin would be cerebral accidents, spinal cord injury, tumors, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, encephalitis, dementias, cerebellar degeneration and epilepsy.
Two major pathways involved in initiating penile erection-
Psychogenic- in which there is involvement of visual or auditory inputs that interface with the organizing regions of the brain.
Reflexogenic- in which erection involves genital sensory stimulation through a spinal cord reflex.
VASCULAR DISORDERS
- Hypertension
- Congestive Heart Failure
- Cerebrovascular Disease
- Coronary Artery Disease
Erectile dysfunction can be an early sign of current or future heart problems. Erectile dysfunction preceding heart problems is often due to the dysfunction of the inner lining of the blood vessels (endothelium) and smooth muscles. This endothelial dysfunction leads to the inadequate blood supply to the heart and impaired blood flow to the penis and results in atherosclerosis.
IATROGENIC
Prostate Cancer- Prostate cancer does not cause erectile dysfunction but its (prostate cancer) treatment can affect the erectile function. The components of erectile function that are affected include-
- Libido (sex drive)- due to the decreased levels of testosterones.
- Orgasm (climax)- due to the lack of firm erections.
- Ejaculation- due to the lack of erection, minimal ejaculation, removal or irradiation of prostate and vesicles.
- Mechanical ability- due to lack of ability to achieve correct erection that is affected by removal of irradiation therapy.
PROSTECTOMY
Men are treated with what is termed a “nerve-sparing” prostatectomy. The goal of the procedure is to take the prostate and seminal vesicles out while sparing the nerves adjacent to the prostate. Approximately 50% of men who have the ability to have an erection before surgery will maintain this ability long-term. This number can increase or decrease based on age, obesity, and the ability to spare the nerves. In general, men with lower-risk prostate cancer have higher rates than average of erectile function given it is easier to spare the nerves. In contrast, men with high-risk prostate cancer it is often more challenging to spare the nerves as the tumor may have spread past the nerves outside the prostate capsule and erectile function rates are lower than average.
SMOKING and ERECTILE DYSFUNCTION
Smoking damage our blood vessels leading to the poor blood supply resulting in erectile dysfunction. The contents and chemicals in the cigarette/bidi/cigar smoke injure the inner lining of the blood vessels resulting in improper flow of blood in the penile region, thus resulting in erectile dysfunction.
ALCOHOL and ERECTILE DYSFUNCTION
Alcohol is a depressant, decrease sexual desire and makes it difficult to achieve erections or reach an orgasm while under the influence. Overdoing it on booze is a common cause of erectile dysfunction. During erection penis is filled with blood and the vessels close preventing backflow so that erection stays for longer time. Overconsumption allows more of blood flow to enter penile region but back flow is not prevented. Intake of more than 40 units (400ml of pure
alcohol/week) doubles the risk of erectile dysfunction in comparison to moderate drinkers and those who don’t drink.
DRUGS and ERECTILE DYSFUNCTION
Drugs that cause erectile dysfunction-
Diuretics and high blood pressure drugs
- Hydrochlorothiazide
- Triamterene
- Furosemide
- Bumetanide
- Guanfacine
- Methyldopa
- Clonidine
- Verapamil
- Nifedipine
- Hydralazine
- Captopril
- Enalapril
- Metoprolol
- Propranolol
- Labetalol
- Atenolol
- Phenoxybenzamine
- Spironolactone
Antidepressants, anti-anxiety drugs, and antiepileptic drug
- Fluoxetine
- Tranylcypromine
- Sertraline
- Isocarboxazid
- Amitriptyline
- Amoxipine
- Clomipramine
- Desipramine
- Nortriptyline
- Phenelzine
- Buspirone
- Chlordiazepoxide
- Clorazepate
- Diazepam
- Doxepin
- Imipramine
- Lorazepam
- Oxazepam
- Phenytoin
Antihistamines
- Dimehydrinate
- Diphenhydramine
- Hydroxyzine
- Meclizine
- Promethazine
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Parkinson's disease medications
- Biperiden
- Benztropine
- Trihexyphenidyl
- Procyclidine
- Bromocriptine
- Levodopa
Histamine H2-receptor antagonists
- Cimetidine
- Nizatidine
- Ranitidine
Muscle relaxants
- Cyclobenzaprine
- Orphenadrine
Prostate cancer medications
Chemotherapy drugs
- Busulfan
- Cyclophosphamide
Other drugs-
- Alcohol
- Amphetamines
- Barbiturates
- Cocaine
- Marijuana
- Methadone
- Nicotine
- Opiates
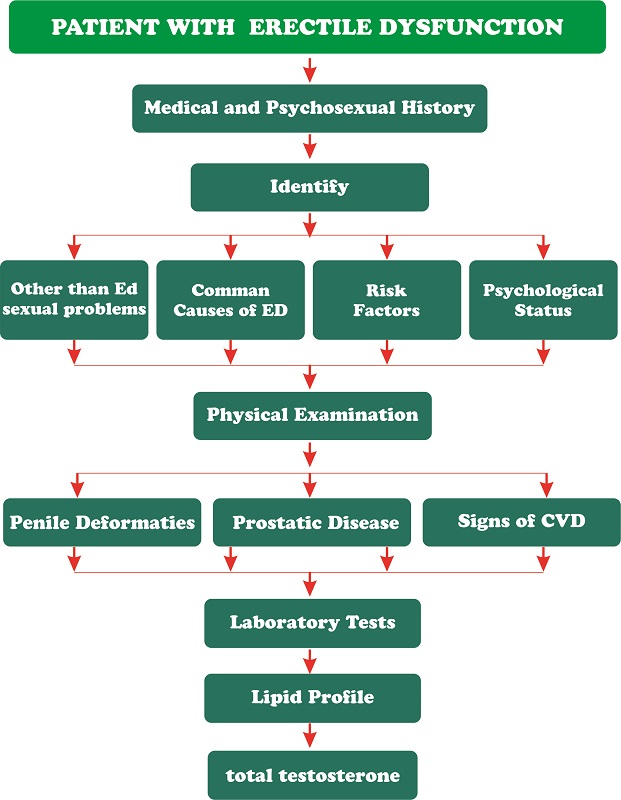
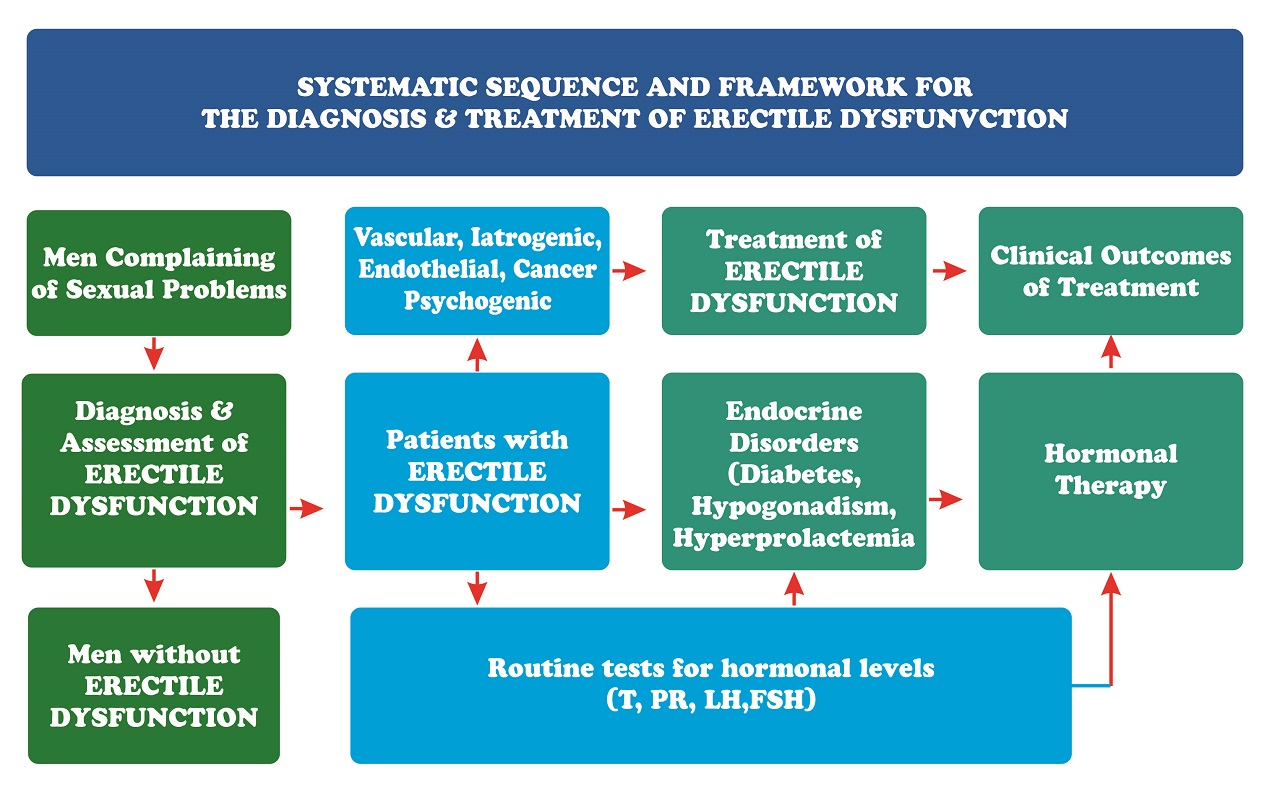
EVALUATION OF PATIENTS WITH ERECTILE DYSFUNCTION
SYSTEMATIC SEQUENCE AND FRAMEWORK FOR DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF ERECTILE DYSFUNCTION :
LIFESTYLE AND DIETARY CHANGES REQUIRED TO CURE ERECTILEDYSFUNCTION
- Quit smoking, limit intake of alcohol to less than 40 units per week (400ml of pure alcohol), balanced diet, brisk walk/cardio/yoga/exercise and proper sleep (7-8 hours).
- Everyday must intake of- 1-2 walnuts, 10-15 almonds, 2-3 figs, 1-2 dates and 200-250 grams of fruits, except banana.
- Weekly must intake of broccoli, fish, and black lentils (kali urad ki daal).